Education, curiously, is one of those subjects on which the divide between the reactionary mindset and the mainstream conservative mindset is starkest.
As far as I can tell, there seem to be three main explanations for why some schools perform poorly.
The leftist mindset is that the problem with "bad schools" (where this is usually taken to mean "schools with poor measures of student academic achievement) is a lack of resources. School funding is tied to property taxes, so rich schools get more money than poor ones, and that's why they perform better. More money will let them buy textbooks, and ipads, and hire better teachers, and have art programs which will distract kids from joining violent gangs, etc.
Of course, this runs up against the problem that we've been throwing money into education, hand over fist, for decades, with literally nothing to show for it. As Scott Alexander discussed a few weeks ago in his post on cost disease:
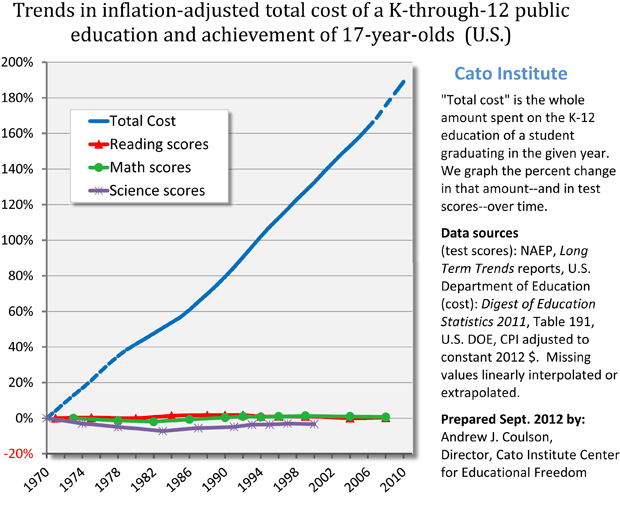
Maybe another 50% increase and we'll finally Fix The Schools™!
And then there's the mainstream conservative answer: the problem with bad schools is bad teachers and bad incentives. The teachers unions are powerful, and the Democrats are beholden to them, which means that there's no competition across schools, no ability to fire underperforming teachers, no incentives for better performance etc.
This of course runs into the problem that if this were the main driver of educational differences, then states where the Democrats have strong political power should do worse. Do they?
No. If you take, say 2015 NAEP 8th Grade Mathematics Scores (available here) and correlate them with 2016 Democratic Presidential Vote Shares (available here), you get a whopping correlation of -0.0595. If you're a regression guy, if you regress mathematics test scores on vote percentage, the t-stat is a paltry -0.417, with an R-squared of 0.0035.
But even this overstates the case, because DC is a huge outlier in vote share at 90.48%, and an absolute sinkhole in terms of test scores. If you take DC out, the correlation is actually positive, at 0.183 (though the t-stat on the regression is still insignificant, at 1.29). If you use 2012 vote shares, which were perhaps more usual, the correlation increases to 0.214 excluding DC, and the t-stat is 1.52. That is to say, more Democratic states do, if anything, slightly better, though the effect isn't particularly strong. You can see this just by ranking the states:
| State | NAEP Math | Dem. Vote Share |
| Massachusetts | 297 | 60.01% |
| Minnesota | 294 | 46.44% |
| New Hampshire | 294 | 46.98% |
| New Jersey | 293 | 54.99% |
| Vermont | 290 | 55.72% |
| Wisconsin | 289 | 46.45% |
| North Dakota | 288 | 27.23% |
| Virginia | 288 | 49.75% |
| Indiana | 287 | 37.91% |
| Montana | 287 | 35.75% |
| Washington | 287 | 54.30% |
| Wyoming | 287 | 21.63% |
| Colorado | 286 | 48.16% |
| Iowa | 286 | 41.74% |
| Nebraska | 286 | 33.70% |
| Utah | 286 | 27.46% |
| Maine | 285 | 47.83% |
| Ohio | 285 | 43.56% |
| South Dakota | 285 | 31.74% |
| Connecticut | 284 | 54.57% |
| Idaho | 284 | 27.49% |
| Kansas | 284 | 36.05% |
| Pennsylvania | 284 | 47.85% |
| Texas | 284 | 43.24% |
| Arizona | 283 | 45.13% |
| Maryland | 283 | 60.33% |
| Oregon | 283 | 50.07% |
| Illinois | 282 | 55.83% |
| Missouri | 281 | 38.14% |
| North Carolina | 281 | 46.17% |
| Rhode Island | 281 | 54.41% |
| Alaska | 280 | 36.55% |
| Delaware | 280 | 53.18% |
| New York | 280 | 58.40% |
| Georgia | 279 | 45.64% |
| Hawaii | 279 | 62.22% |
| Kentucky | 278 | 32.68% |
| Michigan | 278 | 47.27% |
| Tennessee | 278 | 34.72% |
| South Carolina | 276 | 40.67% |
| Arkansas | 275 | 33.65% |
| California | 275 | 61.73% |
| Florida | 275 | 47.82% |
| Nevada | 275 | 47.92% |
| Oklahoma | 275 | 28.93% |
| Mississippi | 271 | 40.11% |
| New Mexico | 271 | 48.26% |
| West Virginia | 271 | 26.48% |
| Louisiana | 268 | 38.45% |
| Alabama | 267 | 34.36% |
| District of Columbia | 263 | 90.48% |
Admittedly there's a lot more variables you'd want to throw into the regression, but still, the univariate big picture doesn't look like the Republican story either.
So what's the reactionary position on why there are bad schools?
Bad schools are primarily due to bad students. Some students are dumb, unruly, lazy, dysfunctional brats. They can't learn, won't learn, and don't learn. You don't even need to take a strong stance on why these differences arise, but just assume that by the time the kids arrive at school, some of them are just a drain and a menace on everyone around them.
And for some reason, this explanation is considered anathema to most right-thinking people. How can you say anything so mean? All students have the potential to succeed, if only they're given the right circumstances!
If the reactionary position strikes you as excessively unkind (especially if its unkindness makes you flinch from accepting its possible truth), I want you to try the following thought experiment.
When you think of "schools", what mental picture comes to mind?
I suspect you are thinking of an idealised brochure, a smiling child at a desk, something that would fit easily as an advertisement for a charity on the side of a bus. The kid is also likely to be young, probably around 5-8 years old, bright-eyed at the world.
Stop thinking of that. Schools aren't like that.
Okay, so what are schools like?
You don't need me to tell you. You've been to one.
To borrow an idea from the War Nerd (when he was explaining why it was easy to get young men to fight and die in wars): if you want to think of schools, think of your 9th grade PE class.
Who was in that class? There were some good students, some of your friends that you think fondly of. If you're reading this blog, chances are both you and your friends were pretty high achieving.
Then there were some middle of the road kids, who were nice enough, and filled out the fat part of the bell curve.
Then there was almost certainly a solid rump of kids best described as complete dickheads. Dumb, mean, idiots. That bully who liked to pick on the young kids. That big punk who stole your friend's bike tire. That guy who was thick as two planks, and boasted about taking a crap on some stranger's car while drunk one Saturday night.
Now, think of just those scumbags, because these are almost certainly the underperforming students we're trying to fix. Imagine that you're designing education policy. How can you improve the educational outcomes of those students? Are they suddenly going to apply themselves more if higher property taxes provide them with a free iPad? Are they about to dive into calculus if only they can find some inspiring young teacher with hip and fresh real world examples of differential equations?
Of course they're not. They're just idiots who will make life miserable for whoever is around them.
If your school has too many such students, it is probably going to be a "bad school". Now, at this stage of argumentation, it is still a matter of conjecture that the scumbag kids of the world are not spread exactly uniformly across every single school district. But is the idea so outlandish? Do you think the adult scumbags are spread precisely uniformly across every neighbourhood and state? Perhaps this matches your experience of traveling around your city or country, but somehow I doubt it. If it were true, you should feel approximately equally happy moving to any neighbourhood in your city, or any state in the country, since everyone is basically the same! Yeah right. And if the annoying adults aren't distributed uniformly, why should the kids be? The first law of behavioral genetics doesn't go away just because you're feeling sentimental about all kids being nice at heart. And given the capacity of nasty kids to have enormous disruptive negative spillovers on the kids around them, it's not clear how much of a difference in distribution you would need to affect the aggregate outcomes.
But even if you think of the whole distribution of students (rather than just the left tail), did that distribution seem like something pretty fixed over your schooling, or something with a lot of year-to-year variation? Did the students in the bottom third of the class in one year ever suddenly jump to the top third the next year as a result of a really good teacher? Or would you say that the personal traits, and relative test scores, of the students in your class were approximately stable in rank order over your whole school career? How confident are you that your treatment could upset last year's rank order by very much?
If your education policy doesn't seem like it will work on the ne'er-do-well kids in your 9th grade PE class, it's probably not going to work at all.
And thinking about those kids is an incredibly grounding reality check to cure multi-billion dollar sentimental nonsense that every kid is just wanting to get the best possible education in life. Some are. Some aren't. It's not that every child who does badly at school is also mean and of poor character. But thinking about the ones that are is the best cure for hazy, rose-tinted thinking on the subject. It makes it easier to focus on the sheer stubbornness of the problem at hand.
None of this means that the reactionary position is the only difference across schools, or that there isn't any role for other factors. But let's just say that it's a hypothesis that seems like it might be worth considering more than currently is done, at least in the public discourse.
None of this means that the reactionary position is the only difference across schools, or that there isn't any role for other factors. But let's just say that it's a hypothesis that seems like it might be worth considering more than currently is done, at least in the public discourse.
It is self-evident that the world has a substantial fraction of dickheads in it.
All of those dickheads were 10 years old once.
Most of them were probably dickheads back then too.