Out of the many oddities of the democratic process in the west, two points stand out.
First, the average citizen has very little idea about how his government works.
Second, the average citizen has very little idea that he has very little idea about how his government works.
If pushed, I think the second point is the more remarkable one. It is quite an amazing feat of propaganda. The evidence that government doesn't work the way most people assume it does is all around them. But they somehow manage to never notice.
I think it comes back to the distinction between the real and the nominal organisational chart of government.
In the case of China, your average American understands that he has no idea how its government functionally operates. Furthermore, he also assumes, rightly, not to trust the notional description coming from China of how its government works. America has a Congress. China, as it turns out, also has a Congress. The average American, however, is likely to be correctly skeptical about whether this body is actually exercising any substantial decision-making authority. He suspects that finding out how China's government actually works is likely to be a difficult task, and one that will require some considerable research.
But for some reason, these thoughts never seem to occur to him about his own government, even though every single one would be just as appropriate.
In the case of America, he has been inculcated with the official organisational chart since birth. There are three branches - legislative, judicial and executive. They exist in a separation of powers, and all are ultimately answerable to the voters, who elect Congress and the President, and thus can eventually appoint all the Supreme Court nominees.
Granted, this is not an absurd description. All these bodies really do exist. At some point, perhaps, this was how governmental decisions in America were actually made.
On the other hand, our hypothetical reader would need to only click on a news website on almost any given day to find events that seem wholly inconsistent with this being the set of people who in practice make decisions as to how government runs.
To take but one example, it was recently announced that Harriet Tubman will replace Andrew Jackson on the $20 bill.
This, of course, raises a number of questions that the average person almost certainly never gets around to asking, but probably should.
Let's start with the basics.
Who, exactly, decided that this would happen?
As a beginning, he has absolutely no idea. Without googling, he couldn't even name the office behind this decision.
Reading through the article, we're told that this was announced by Treasury Secretary Jack Lew. Hands up, nice and high, if you've ever heard that name before.
More to the point, being announced by Jack Lew is not the same as being decided by Jack Lew. If it were just decided by Jack Lew, then we can somehow finagle all this akwardly into the notional chart. Obama appointed Lew, he could fire him (perhaps - who knows) and get someone else in who would put Jackson back on.
But how do you know who else was involved in this decision? Are you sure it was just Lew? There are 86,000 people working at the Treasury. You're certain it was just the top guy, on his own, who came up with the plan? Let's be honest, that seems pretty damn unlikely. If every decision is made singlehandedly from the top, what on earth are those 86,000 people doing each day?
If you fire Lew, it's possible the plan gets reversed. It's also possible that you've just fired the guy who's the spokesman, or the frontman for the operation. He'll just be replaced by someone else, and the show will merrily go on.
But even the 'treasury employees make the decision' model seems a little too neat. Indeed, the Washington Post article lists a number of groups and people that seem wholly alien to how this process is meant to work, including:
-Kari Winter, a professor who studies slavery at the University of Buffalo
-A viral campaign by a group "Women on $20s"
-Ben Bernanke
-A musical about Alexander Hamilton by Lin-Manuel Miranda, who apparently was personally contacted by Lew in the leadup to this decision (when it was decided that Hamilton wasn't getting ditched from the $10)
-Liz Maatz, vice president of government relations for the American Association of University Women
One of two things seems true. Either these people are part of the actual decision-making process. Or the Washington Post is just asking random nobodies to give their opinion
Which do you suppose is more likely? Who do you suppose knows more about how government operates, you or the Washington Post?
Because, dear average interlocutor, let us get to the heart of the matter.
You still believe the notional org chart, because this is all you know. This decision must come from the Secretary of Treasury, which comes from the President, which comes from us, the voters. Ergo, we can reverse this by voting for Trump in November, who certainly wouldn't put up with this nonsense.
Perhaps.
But didn't they tell you this when you voted for George W. Bush twice? Looking back, what exactly did that get you?
You would do better to start by admitting some basic truths.
You have no idea who made this decision.
You have no idea how, or if, it could be reversed.
You have no idea who is actually governing you.
And if you've gotten that far, why are you so sure that voting will fix it?
One pound of inference, no more, no less. No humbug, no cant, but only inference. This task done, and he would go free.
Saturday, April 30, 2016
The perils of reading the fake government org chart
Saturday, April 16, 2016
Subtle Hallmarks of Narcissism
I once had a friend who was at least at the sub-clinical level of narcissism (by my amateur reckoning of the matter). He was very clever, and got easily annoyed with people who thought were stupider than him, or who were wasting his time.
One of the things that manifested itself very strongly was that he was enormously sure of his own opinions. People who disagreed were nearly always morons, and were strongly mocked. This wasn't just on objective beliefs either - matters of taste, however arbitrary, were treated with similar absolutism. The gap between his taste and objective quality, in his mind, was zero. This would even occur when extreme positions were taken on otherwise similar issues. Because he was brilliant, his opinion on these matters must be right. He was also very funny, gregarious when he wanted to be, and and a keen reader of other people. I still count him as a friend, so don't get the wrong idea here.
So how do you tell that someone is narcissistic, rather than just stubborn and opinionated? There is, after all, substantial overlap. Do you fail to change your mind just because you believe things very strongly, or do you fail to change your mind because your belief in your own brilliance means that you simply can't contemplate the possibility of you being wrong?
One trait I observed was that when he did change his mind, he rarely acknowledged it for very long (if at all), and then proceeded to proselytize the new view with all the fervor previously given to the old. The self-image must be preserved at all costs. What you believe isn't strictly important. What's more important is that you're a clever, insightful person who makes good choices.
But that, to my mind, wasn't the key giveaway about narcissism.
The guy was a perfectionist in his job, and thus slow to actually complete projects. At some point, he didn't get promoted, and so was leaving the industry to work elsewhere.
Based on a hunch, I asked him at some point what things he had changed his mind on during his time in the job. I had suspected that it would be nothing at all, but that turned out not to be true.
He told me instead that when he started he had thought that good work would get rewarded, and the competent would rise to the top of the profession. But over time he saw that the senior ranks were just filled by rent-seeking people who had got themselves into positions of authority and expropriated smart, hard-working junior people.
Sensing that I might be on to something, I asked him to clarify something else. Had he learned or changed his mind on anything in a way that had caused him to update negatively about himself?
He paused, and considered the question for a few seconds, quite obviously for the first time. 'No', was his answer, which was the truthful one. He thought he was good, and didn't need to BS with false humility.
And I realised this was the crux of the issue. What he had learned, in other words, was that he was too good for the job he was in.
A narcissist can learn, and a narcissist can change their mind. But they can never change their mind in a way that causes them to update negatively about themselves.
If he had failed in the job, the problem must be the job.
And this also helped explain something else that I suspect is common to narcissists, and possibly to low empathy types who lean towards sociopathic behavior (I truthfully can't always distinguish these two cases cleanly, which shows that I'm not a psychiatrist, just an interested amateur - my friend I put mostly just in the narcissist category). Sophisticated narcissists who are low on empathy can be very good at reading other people, and using this to manipulate them. But every now and again, they'll also make spectacular own-goals in social situations that leave everyone else scratching their heads.
When I tallied up what caused these in the case of my friend, the one thing that he wasn't able to see clearly was what other people thought of him. He thought that everyone loved him, whereas a lot of people didn't. He could read people in general, and he could read what other people thought of themselves, but because his own image of himself was so dominant, it prevented him seeing what others thought of him.
I hereby volunteer as a job interview question 'what is something that you changed your mind on in a way that caused you to update negatively about yourself'. It's one that people won't have a canned answer for, and will tell you whether they're actually able to see their own weaknesses, or whether they lean towards narcissistic self-adulation.
One of the things that manifested itself very strongly was that he was enormously sure of his own opinions. People who disagreed were nearly always morons, and were strongly mocked. This wasn't just on objective beliefs either - matters of taste, however arbitrary, were treated with similar absolutism. The gap between his taste and objective quality, in his mind, was zero. This would even occur when extreme positions were taken on otherwise similar issues. Because he was brilliant, his opinion on these matters must be right. He was also very funny, gregarious when he wanted to be, and and a keen reader of other people. I still count him as a friend, so don't get the wrong idea here.
So how do you tell that someone is narcissistic, rather than just stubborn and opinionated? There is, after all, substantial overlap. Do you fail to change your mind just because you believe things very strongly, or do you fail to change your mind because your belief in your own brilliance means that you simply can't contemplate the possibility of you being wrong?
One trait I observed was that when he did change his mind, he rarely acknowledged it for very long (if at all), and then proceeded to proselytize the new view with all the fervor previously given to the old. The self-image must be preserved at all costs. What you believe isn't strictly important. What's more important is that you're a clever, insightful person who makes good choices.
But that, to my mind, wasn't the key giveaway about narcissism.
The guy was a perfectionist in his job, and thus slow to actually complete projects. At some point, he didn't get promoted, and so was leaving the industry to work elsewhere.
Based on a hunch, I asked him at some point what things he had changed his mind on during his time in the job. I had suspected that it would be nothing at all, but that turned out not to be true.
He told me instead that when he started he had thought that good work would get rewarded, and the competent would rise to the top of the profession. But over time he saw that the senior ranks were just filled by rent-seeking people who had got themselves into positions of authority and expropriated smart, hard-working junior people.
Sensing that I might be on to something, I asked him to clarify something else. Had he learned or changed his mind on anything in a way that had caused him to update negatively about himself?
He paused, and considered the question for a few seconds, quite obviously for the first time. 'No', was his answer, which was the truthful one. He thought he was good, and didn't need to BS with false humility.
And I realised this was the crux of the issue. What he had learned, in other words, was that he was too good for the job he was in.
A narcissist can learn, and a narcissist can change their mind. But they can never change their mind in a way that causes them to update negatively about themselves.
If he had failed in the job, the problem must be the job.
And this also helped explain something else that I suspect is common to narcissists, and possibly to low empathy types who lean towards sociopathic behavior (I truthfully can't always distinguish these two cases cleanly, which shows that I'm not a psychiatrist, just an interested amateur - my friend I put mostly just in the narcissist category). Sophisticated narcissists who are low on empathy can be very good at reading other people, and using this to manipulate them. But every now and again, they'll also make spectacular own-goals in social situations that leave everyone else scratching their heads.
When I tallied up what caused these in the case of my friend, the one thing that he wasn't able to see clearly was what other people thought of him. He thought that everyone loved him, whereas a lot of people didn't. He could read people in general, and he could read what other people thought of themselves, but because his own image of himself was so dominant, it prevented him seeing what others thought of him.
I hereby volunteer as a job interview question 'what is something that you changed your mind on in a way that caused you to update negatively about yourself'. It's one that people won't have a canned answer for, and will tell you whether they're actually able to see their own weaknesses, or whether they lean towards narcissistic self-adulation.
Thursday, March 31, 2016
The Other Great Geographic Discontinuity
Discontinuities are interesting things. When small differences in inputs result in large differences in outputs, it can sometimes give hints as to what exactly is causing what.
For instance, Douglas Almond's great paper on the in-utero effects of the Spanish Flu gets you mostly convinced just by a single picture
The ideal case observes a sharp discontinuity in a single input variable and examines the effect on the output. Economists search for these perfectly clean cases like financial traders search for arbitrage. They find them about as often, too.
But sometimes you get a second best instance - a case where a good fraction of the inputs stay smooth and continuous, and yet you observe a discontinuous shift in the output. This suggests that one of the remaining variables is having a large effect.
This is especially true in the case of development. The classic problem, concisely stated, is that goods go together and bads go together. In other words, countries tend to have good governance, good rule of law, a free press, low corruption, etc. or they have none of these things.
Boosters of the polite consensus wisdom occasionally enjoy pointing out the difference in light patterns between North and South Korea.

It is indeed a striking one. Scott Alexander cited it in his Anti-Reactionary FAQ as supporting the proposition that the quasi-monarchy of North Korea seems to result in much worse outcomes than the capitalist social democracy of South Korea.
Fair enough. So it does. Though of course what we're really seeing is the sum of all the differences between the North and South since the Korean War. The main quibble is the extent to which Kim Jong-Un is a good representation of monarchy as a system of government, but I take Alexander's point.
But if you're going to play that game, you have to take the comparisons that are not flattering to your world view, as well as the ones that are.
One such equally stark comparison is between Haiti and the Dominican Republic.

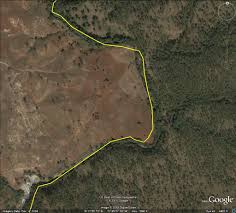
No, they didn't draw the border at some magically discontinuous shift in micro-climate. This is all one island of Hispaniola, split into two parts. It's just that the Haitians deforested their part of the island, leaving the land looking like it was denuded by a plague of locusts. The Dominicans, however, didn't.
And this is the start of a series of differences that are not quite as stark as North and South Korea, but they're pretty darn stark nonetheless. Haiti is supremely screwed, as bad as anywhere in the Third World. We're talking GDP per capita of $661 and life expectancy of 63 screwed. The Dominican Republic, by contrast is at $5442 and 74. Not exactly first world standards, but functional enough that westerners want to go there on holidays. To slightly modify the Hilltop Hoods - like a free trip to Port-Au-Prince, you don't want it.
And there basically is no polite explanation for why this is. The standard banalities about the causes of poverty don't get you very far. If Haiti's problem is that it was colonialized, so was the Dominican Republic. Admittedly the Haitian part was run by the French for more of its history, versus the Dominican Republic being run by the Spanish. But people don't usually clamor to attribute strong economic success to Spanish colonialism. In fact, the Dominican Republic was run as a colony for considerably longer, as recently as 1865 (compared with Haiti, which kicked out the French for the last time in 1804). Indeed, Haiti actually invaded and ran the Dominican Republic from 1821-1844, and got to implement some of its disastrous policies then.
The other sob stories don't get you much further either. Both areas had a lot of slaves. Both were administered by the US during the 20th century. And while the Dominican Republic produced a lot more sugar during the 20th century, this seems better understood as effect rather than just cause, as Haiti produced lots of sugar during the 18th century, and climate-wise could have done so again.
So since the countries were united for most of their history, one must expect that the causes might seem to be differences that were more pronounced after 1844.
First off, Haiti had killed most of its white population in a genocide, and added to its constitution in 1804 a clause that whites could not own property. Another country imposed this recently in the wake of similar genocidal behavior. You might almost conclude that this is a disastrous policy. It was imposed in the Dominican Republic too in 1821 when Haiti took over, but they hadn't gone for the full genocidal answer of killing all the whites. So even though lots of the Spanish left after their stuff was confiscated, enough of them stuck around, and eventually managed to successfully gain independence from Haiti in 1844. The Dominican Republic tended to be mostly governed by its richer and better-educated Spanish elite for much of its history, whereas Haiti mostly was governed by the descendants of slaves (either black or mulatto). Just look at the pictures of some of the presidents of the Dominican Republic. No matter how you cut it or interpret it, the difference is striking.










etc.
Now look at some of the corresponding presidents of Haiti










Of course, a closer examination makes all this a bit murkier. Even after most of the leaders above, both countries were sufficiently dysfunctional that the US chose to invade, in 1915 and 1916. Equally dysfunctional? It's hard to say, since this was the era before great GDP figures. In terms of long-serving leaders during the 20th century, they had different paths. Rafael Trujillo seems to have looked somewhat like Pinochet, brutal but effective. Papa Doc Duvalier seems like a cross between Idi Amin and Robert Mugabe, repulsive in every possible way. It turns out that being a black nationalist intent on driving out the mulatto elite tends to just produce a mass emigration of the educated parts of the populace. We've heard about that one before too. It's not for nothing that I compared him to Mugabe. Maybe this is the main difference, these two men. It's hard to say.
So we get to the end and don't get the neat schadenfreude of Scott Alexander's simple narrative. In the end, we observe a discontinuous outcome, not a discontinuous input, and identification still eludes us. I am not nearly enough of an expert to compile anything like an exhaustive list of the differences between the countries to say for sure what is driving it. And yet, the aerial photographs remain. Something is producing enormously discontinuous outcomes across small geographical differences. And if you dislike the things I've raised, does that not just deepen the puzzle? Admit it, my progressive friend - you don't have a satisfactory explanation for the difference, do you?
By any measure, Haiti has been profoundly misgoverned. The Dominican Republic serves as Banquo's Ghost, reminding us awkwardly that it didn't have to end up this way. It is not a happy tale, and the lessons, if there are any, don't seem to support the standard leftist narratives of why the third world is poor. No wonder you never hear about it.
Actually, that's not quite right.
You do occasionally hear about it, in the form of editorials in lefty western newspapers excoriating the Dominican Republic for its racism in deporting Haitian illegal immigrants, notwithstanding the fact that, by US definitions of race, the Dominican Republic itself is 80% black.
Yep, racism. That's the key to understanding all this, according to our intellectually bankrupt intellectuals. The overwhelmingly black Dominican Republic must be cast in the role of racist oppressor, because that's the only way by which the left can understand Haitian poverty, or indeed any poverty at all.
With such brilliant insights among our elites, I have no doubt that Haiti will soon be returned to the days when it produced leaders like Thomas-Alexandre Dumas and Alexandre Dumas.
I wouldn't hold your breath. Haiti has been collectively holding its breath for 200 years.
For instance, Douglas Almond's great paper on the in-utero effects of the Spanish Flu gets you mostly convinced just by a single picture
The ideal case observes a sharp discontinuity in a single input variable and examines the effect on the output. Economists search for these perfectly clean cases like financial traders search for arbitrage. They find them about as often, too.
But sometimes you get a second best instance - a case where a good fraction of the inputs stay smooth and continuous, and yet you observe a discontinuous shift in the output. This suggests that one of the remaining variables is having a large effect.
This is especially true in the case of development. The classic problem, concisely stated, is that goods go together and bads go together. In other words, countries tend to have good governance, good rule of law, a free press, low corruption, etc. or they have none of these things.
Boosters of the polite consensus wisdom occasionally enjoy pointing out the difference in light patterns between North and South Korea.

It is indeed a striking one. Scott Alexander cited it in his Anti-Reactionary FAQ as supporting the proposition that the quasi-monarchy of North Korea seems to result in much worse outcomes than the capitalist social democracy of South Korea.
Fair enough. So it does. Though of course what we're really seeing is the sum of all the differences between the North and South since the Korean War. The main quibble is the extent to which Kim Jong-Un is a good representation of monarchy as a system of government, but I take Alexander's point.
But if you're going to play that game, you have to take the comparisons that are not flattering to your world view, as well as the ones that are.
One such equally stark comparison is between Haiti and the Dominican Republic.

No, they didn't draw the border at some magically discontinuous shift in micro-climate. This is all one island of Hispaniola, split into two parts. It's just that the Haitians deforested their part of the island, leaving the land looking like it was denuded by a plague of locusts. The Dominicans, however, didn't.
And this is the start of a series of differences that are not quite as stark as North and South Korea, but they're pretty darn stark nonetheless. Haiti is supremely screwed, as bad as anywhere in the Third World. We're talking GDP per capita of $661 and life expectancy of 63 screwed. The Dominican Republic, by contrast is at $5442 and 74. Not exactly first world standards, but functional enough that westerners want to go there on holidays. To slightly modify the Hilltop Hoods - like a free trip to Port-Au-Prince, you don't want it.
And there basically is no polite explanation for why this is. The standard banalities about the causes of poverty don't get you very far. If Haiti's problem is that it was colonialized, so was the Dominican Republic. Admittedly the Haitian part was run by the French for more of its history, versus the Dominican Republic being run by the Spanish. But people don't usually clamor to attribute strong economic success to Spanish colonialism. In fact, the Dominican Republic was run as a colony for considerably longer, as recently as 1865 (compared with Haiti, which kicked out the French for the last time in 1804). Indeed, Haiti actually invaded and ran the Dominican Republic from 1821-1844, and got to implement some of its disastrous policies then.
The other sob stories don't get you much further either. Both areas had a lot of slaves. Both were administered by the US during the 20th century. And while the Dominican Republic produced a lot more sugar during the 20th century, this seems better understood as effect rather than just cause, as Haiti produced lots of sugar during the 18th century, and climate-wise could have done so again.
So since the countries were united for most of their history, one must expect that the causes might seem to be differences that were more pronounced after 1844.
First off, Haiti had killed most of its white population in a genocide, and added to its constitution in 1804 a clause that whites could not own property. Another country imposed this recently in the wake of similar genocidal behavior. You might almost conclude that this is a disastrous policy. It was imposed in the Dominican Republic too in 1821 when Haiti took over, but they hadn't gone for the full genocidal answer of killing all the whites. So even though lots of the Spanish left after their stuff was confiscated, enough of them stuck around, and eventually managed to successfully gain independence from Haiti in 1844. The Dominican Republic tended to be mostly governed by its richer and better-educated Spanish elite for much of its history, whereas Haiti mostly was governed by the descendants of slaves (either black or mulatto). Just look at the pictures of some of the presidents of the Dominican Republic. No matter how you cut it or interpret it, the difference is striking.










etc.
Now look at some of the corresponding presidents of Haiti










Of course, a closer examination makes all this a bit murkier. Even after most of the leaders above, both countries were sufficiently dysfunctional that the US chose to invade, in 1915 and 1916. Equally dysfunctional? It's hard to say, since this was the era before great GDP figures. In terms of long-serving leaders during the 20th century, they had different paths. Rafael Trujillo seems to have looked somewhat like Pinochet, brutal but effective. Papa Doc Duvalier seems like a cross between Idi Amin and Robert Mugabe, repulsive in every possible way. It turns out that being a black nationalist intent on driving out the mulatto elite tends to just produce a mass emigration of the educated parts of the populace. We've heard about that one before too. It's not for nothing that I compared him to Mugabe. Maybe this is the main difference, these two men. It's hard to say.
So we get to the end and don't get the neat schadenfreude of Scott Alexander's simple narrative. In the end, we observe a discontinuous outcome, not a discontinuous input, and identification still eludes us. I am not nearly enough of an expert to compile anything like an exhaustive list of the differences between the countries to say for sure what is driving it. And yet, the aerial photographs remain. Something is producing enormously discontinuous outcomes across small geographical differences. And if you dislike the things I've raised, does that not just deepen the puzzle? Admit it, my progressive friend - you don't have a satisfactory explanation for the difference, do you?
By any measure, Haiti has been profoundly misgoverned. The Dominican Republic serves as Banquo's Ghost, reminding us awkwardly that it didn't have to end up this way. It is not a happy tale, and the lessons, if there are any, don't seem to support the standard leftist narratives of why the third world is poor. No wonder you never hear about it.
Actually, that's not quite right.
You do occasionally hear about it, in the form of editorials in lefty western newspapers excoriating the Dominican Republic for its racism in deporting Haitian illegal immigrants, notwithstanding the fact that, by US definitions of race, the Dominican Republic itself is 80% black.
Yep, racism. That's the key to understanding all this, according to our intellectually bankrupt intellectuals. The overwhelmingly black Dominican Republic must be cast in the role of racist oppressor, because that's the only way by which the left can understand Haitian poverty, or indeed any poverty at all.
With such brilliant insights among our elites, I have no doubt that Haiti will soon be returned to the days when it produced leaders like Thomas-Alexandre Dumas and Alexandre Dumas.
I wouldn't hold your breath. Haiti has been collectively holding its breath for 200 years.
Labels:
Development,
Government,
History,
Sketch of a Model,
The Third World
Thursday, March 24, 2016
"Hamilton" as American Propaganda
I recently saw the musical 'Hamilton', which was an enjoyable depiction of American nostalgia for its own myths. That much isn't new. What's new is that this is being successfully marketed to the current generation of narcissistic millennials. Getting them to take any interest in history beyond their own short life span, let alone past the 20th century, is quite a feat, even if what they end up learning ends up having a healthy dose of nonsense.
As both a foreigner and a reactionary, it's interesting to see the American founding myths in all their peculiar detail. Identifying the nonsense stories other people accept uncritically about their own history is much easier than identifying one's own. The US ones are particularly interesting to me - I have a strong fondness for this country, but I still view it as as an outsider, as a) I came across this stuff much later in life, and b) my summary of the American Revolution in one sentence is "the bad guys won". Incidentally, this would make a great tagline for a future reactionary version of the play, 'Hutchinson: The Musical".
Of course, if you want to get the record set straight, Moldbug is of course the best source. And with a little of the alternative perspective on the matter, the most interesting thing about the play is what gets left out.
The second most neglected perspective in the history of American Revolution is the Loyalists. For the most part, they simply don't exist. "America" was fighting King George. The fact that there were substantial numbers of native-born Americans who were philosophically and practically opposed to the War of Independence gets mostly elided. How many, exactly? Hard to say. I've seen numbers floated around as being 20%, but this doesn't mean that 80% were Patriots, as a large number were on the fence. I'd take all these numbers with a grain of salt.
The musical actually does better than I expected - there's one scene where a Loyalist is giving a speech in opposition to the Congress (unpersuasively, of course) , and he then gets mocked by Hamilton. That they don't present a good case for the opposition is not surprising - that they acknowledge the opposition existed, and was American, was frankly a pleasant surprise.
So the Loyalists, uncharacteristically, weren't the Elephant in the Room being ignored here. What was, then? What is the faction you almost never hear about in the re-telling of the American Revolution?
The answer is simple: British Parliament.
Britain in the musical, like in nearly all popular retellings, is represented by King George III. He is depicted as being in charge of the whole affair, pulling all the strings from across the sea. It's like the whole musical, like the country itself, lives in a bizarre alternative universe where the Cavaliers somehow won the English Civil War. In reality, the issue had been decided twice, first with King Charles being separated from his head, and then in case the message hadn't been received, again with the Glorious Revolution chasing King James II out of England, all the way to France in fact. By the time of the American Revolution, the verdict had been in for over a century - when push came to shove, Parliament was in charge.
But you can see clearly why this very quickly becomes awkward for the standard narrative. The American revolution was about establishing democracy (praise be upon it) for the first time ever! Except that the government being overthrown was in fact democratic, in various different forms, from at least 1215 onwards. Quite a pickle, no?
Aha, the apologists respond, but there was no democratic representation among the Americans. No taxation without representation, and all that. What an injustice! I'll let Mr Hutchinson field this one:
Massachusetts: No Taxation without Representation!
Britain: Hmm. Would you like some representation then?
Massachusetts: No, absolutely not, it would never work!
Comedy gold.
So if the big injustice that Alexander Hamilton was fighting against wasn't really a lack of democratic representation, what exactly was it?
Beats me. Beats Hutchinson too.
And this is the odd sense that comes after all the great songs are over. It's the same feeling I had years ago watching Michael Moore documentaries. In the moment, the strange web of narrative seems oddly compelling, until you leave the theatre and try to distill it into a sentence. And lo and behold, the main thesis is that Dylan Klebold and Eric Harris shot up a school because Lockheed Martin had a factory somewhere nearby making parts for satellites. Phrased thus, you realise that this is an insane argument, and you can't believe you fell for it in the first place.
That's where I get to on Hamilton. Once you leave the theatre, odd reactionary thoughts come back in. You mean he was a hardworking immigrant who loved his newfound country so much that he... immediately worked to overthrow its government? Hmm, that doesn't sound so good. Wait, no, he was a poor penniless orphan who wanted to rise up the ranks, and so he realised that helping foment a war and rising up the command would be a great way to do this? Wait, that even worse. Much worse, actually.
The final thought, however, that the honest foreigner must admit to himself, is this: I wonder what equivalent stupidity I've believed about my own history?
Truthfully, I don't quite know. But if I figure it out, I'll let you know.
As both a foreigner and a reactionary, it's interesting to see the American founding myths in all their peculiar detail. Identifying the nonsense stories other people accept uncritically about their own history is much easier than identifying one's own. The US ones are particularly interesting to me - I have a strong fondness for this country, but I still view it as as an outsider, as a) I came across this stuff much later in life, and b) my summary of the American Revolution in one sentence is "the bad guys won". Incidentally, this would make a great tagline for a future reactionary version of the play, 'Hutchinson: The Musical".
Of course, if you want to get the record set straight, Moldbug is of course the best source. And with a little of the alternative perspective on the matter, the most interesting thing about the play is what gets left out.
The second most neglected perspective in the history of American Revolution is the Loyalists. For the most part, they simply don't exist. "America" was fighting King George. The fact that there were substantial numbers of native-born Americans who were philosophically and practically opposed to the War of Independence gets mostly elided. How many, exactly? Hard to say. I've seen numbers floated around as being 20%, but this doesn't mean that 80% were Patriots, as a large number were on the fence. I'd take all these numbers with a grain of salt.
The musical actually does better than I expected - there's one scene where a Loyalist is giving a speech in opposition to the Congress (unpersuasively, of course) , and he then gets mocked by Hamilton. That they don't present a good case for the opposition is not surprising - that they acknowledge the opposition existed, and was American, was frankly a pleasant surprise.
So the Loyalists, uncharacteristically, weren't the Elephant in the Room being ignored here. What was, then? What is the faction you almost never hear about in the re-telling of the American Revolution?
The answer is simple: British Parliament.
Britain in the musical, like in nearly all popular retellings, is represented by King George III. He is depicted as being in charge of the whole affair, pulling all the strings from across the sea. It's like the whole musical, like the country itself, lives in a bizarre alternative universe where the Cavaliers somehow won the English Civil War. In reality, the issue had been decided twice, first with King Charles being separated from his head, and then in case the message hadn't been received, again with the Glorious Revolution chasing King James II out of England, all the way to France in fact. By the time of the American Revolution, the verdict had been in for over a century - when push came to shove, Parliament was in charge.
But you can see clearly why this very quickly becomes awkward for the standard narrative. The American revolution was about establishing democracy (praise be upon it) for the first time ever! Except that the government being overthrown was in fact democratic, in various different forms, from at least 1215 onwards. Quite a pickle, no?
Aha, the apologists respond, but there was no democratic representation among the Americans. No taxation without representation, and all that. What an injustice! I'll let Mr Hutchinson field this one:
The Assembly of Massachusetts Bay, therefore, was the first that took any publick of the Act, and the first which ever took exception to the right of Parliament to impose Duties or Taxes on the Colonies, whilst they had no representatives in the House of Commons. This they did in a letter to their Agent in the summer of 1764, which they took care to print and publish before it was possible for him to receive it. And in this letter they recommend to him a pamphlet, wrote by one of their [6] members, in which there are proposals for admitting representatives from the Colonies to fit in the House of Commons.
I have this special reason, my Lord, for taking notice of this Act of the Massachusetts Assembly; that though an American representation is thrown out as an expedient which might obviate the objections to Taxes upon the Colonies, yet it was only intended to amuse the authority in England; and as soon as it was known to have its advocates here, it was renounced by the colonies, and even by the Assembly of the Colony which first proposed it, as utterly impracticable.In other words:
Massachusetts: No Taxation without Representation!
Britain: Hmm. Would you like some representation then?
Massachusetts: No, absolutely not, it would never work!
Comedy gold.
So if the big injustice that Alexander Hamilton was fighting against wasn't really a lack of democratic representation, what exactly was it?
Beats me. Beats Hutchinson too.
And this is the odd sense that comes after all the great songs are over. It's the same feeling I had years ago watching Michael Moore documentaries. In the moment, the strange web of narrative seems oddly compelling, until you leave the theatre and try to distill it into a sentence. And lo and behold, the main thesis is that Dylan Klebold and Eric Harris shot up a school because Lockheed Martin had a factory somewhere nearby making parts for satellites. Phrased thus, you realise that this is an insane argument, and you can't believe you fell for it in the first place.
That's where I get to on Hamilton. Once you leave the theatre, odd reactionary thoughts come back in. You mean he was a hardworking immigrant who loved his newfound country so much that he... immediately worked to overthrow its government? Hmm, that doesn't sound so good. Wait, no, he was a poor penniless orphan who wanted to rise up the ranks, and so he realised that helping foment a war and rising up the command would be a great way to do this? Wait, that even worse. Much worse, actually.
The final thought, however, that the honest foreigner must admit to himself, is this: I wonder what equivalent stupidity I've believed about my own history?
Truthfully, I don't quite know. But if I figure it out, I'll let you know.
Tuesday, March 1, 2016
Micro-snapshots of personal agency
One of my minor hobbies is noticing small correlations in how people speak that reveal things about them. Some examples here, here and here.
I was reminded of one from a conversation I overheard in an elevator today:
Which reminded me of something I noticed way back in the third grade.
Like all small children, our pencils would often go missing. And when they did, people immediately fell into one of two narratives
a) I lost it.
b) Someone stole it.
I was always in the first category. I assume that I'm just forgetful and careless, which I am.
But some kids were always certain, without any proof, that the world was full of malicious people out to get them, stealing all their pens and pencils.
And if the girl's conversation is anything to go by, I suspect this difference persists later in life.
I may simply be naive about this, and extrapolating from my own mental state. But I can't quite believe that there's that many pen thieves out there in the offices and classrooms of the world. Who are all these people apparently swiping pens? Even the guy's point, which is the better one, seems more obviously explained by the fact that you only notice when a good pen goes missing, and the crummy pens go missing too, but you didn't pay attention because you didn't care.
The first sign that there isn't a pen conspiracy is that pens seem to go missing at approximately the same rate as individual socks go missing in the washing process. And I don't think anyone actually believes that the underpants gnomes are taking them. Things get dropped randomly, or forgotten, or misplaced. That's just life.
But when these kinds of annoying things happen, do you accept that as just part of the random bad luck of life? Do you blame yourself? Or do you blame a conspiracy of others?
I would wager that people who think pens frequently go missing because they get stolen are less likely to accept responsibility for their own screwups in life. I would wager they these people are probably somewhat less self-aware.
That seems like a strong conclusion to draw. It's only a hunch, presented as such. But it's how I'd bet.
Off such small pieces of information are efficient estimates of personality made.
Given enough enough data about the world, nobody is really a mystery.
I was reminded of one from a conversation I overheard in an elevator today:
Girl: I forgot to bring a pen.
Guy: Oh well, we can go back up and get one.
Girl: I used to have a nice one that I'd carry with me.
Guy: For some reason, the crummy pens stick around, while the good pens always disappear.
Girl: Yeah, that's because people always end up taking them.
Which reminded me of something I noticed way back in the third grade.
Like all small children, our pencils would often go missing. And when they did, people immediately fell into one of two narratives
a) I lost it.
b) Someone stole it.
I was always in the first category. I assume that I'm just forgetful and careless, which I am.
But some kids were always certain, without any proof, that the world was full of malicious people out to get them, stealing all their pens and pencils.
And if the girl's conversation is anything to go by, I suspect this difference persists later in life.
I may simply be naive about this, and extrapolating from my own mental state. But I can't quite believe that there's that many pen thieves out there in the offices and classrooms of the world. Who are all these people apparently swiping pens? Even the guy's point, which is the better one, seems more obviously explained by the fact that you only notice when a good pen goes missing, and the crummy pens go missing too, but you didn't pay attention because you didn't care.
The first sign that there isn't a pen conspiracy is that pens seem to go missing at approximately the same rate as individual socks go missing in the washing process. And I don't think anyone actually believes that the underpants gnomes are taking them. Things get dropped randomly, or forgotten, or misplaced. That's just life.
But when these kinds of annoying things happen, do you accept that as just part of the random bad luck of life? Do you blame yourself? Or do you blame a conspiracy of others?
I would wager that people who think pens frequently go missing because they get stolen are less likely to accept responsibility for their own screwups in life. I would wager they these people are probably somewhat less self-aware.
That seems like a strong conclusion to draw. It's only a hunch, presented as such. But it's how I'd bet.
Off such small pieces of information are efficient estimates of personality made.
Given enough enough data about the world, nobody is really a mystery.
Tuesday, February 23, 2016
For Mormonism
The attitude of non-Mormons to Mormonism usually tells you quite a lot about what else they value.
And the critiques are well-rehearsed.
Militant atheists like to mock Mormonism’s odd beliefs about the universe, amply documented (in otherwise quite fair and sympathetic portrayals) in Southpark and The Book of Mormon. The beliefs themselves, including disappearing golden tablets and the like, are not really much more absurd than many other religions. But they are claimed to have happened more recently, which seems to make an unusually large difference. Partly this makes certain events easier to disprove, but I don’t think that’s really it. I think actually most of the difference in perception is psychological. To the rationalist, it is no more plausible that Jesus turned water into wine two thousand years ago than that I turned water into wine yesterday. To the common person, however, the latter seems to require a larger suspension of disbelief – the rest of the scene is suddenly palpable and gets compared with what we know about the modern world. For some reason, with old religions, part of the brain thinks ‘well, who knows what things were like back then’.
Social Justice types tend to berate Mormons for their socially conservative views. They dislike abortion, they dislike gay marriage, they tend to hold to quite traditional views of gender roles. Add in desired talking points to taste on whatever side you like here and this writes itself. I do note, however, that the volume of the criticism they receive seems better explained by the fact that they’re a soft target in social terms and won’t fight back. After Proposition 8 passed in California, lefties angrily protested against the Mormons (who supported it on average), but not against Blacks and Hispanics who also supported it on average (the same is probably true of Muslims too). Interpret how you will.
Myself, I’ve always been far more struck by something much simpler. Nearly all the Mormons I’ve ever met have been really friendly, nice people. And that matters to me, a lot. We’re talking maybe n=20 or 30 by this point. How many groups of people, in any category, can you honestly say that about?
If I were to choose a religion based purely on the personal qualities and behavior of its average adherent, I’m pretty sure that I’d pick Mormonism.
This hypothetical is less absurd than it sounds. It actually corresponds fairly closely to the thought process that atheist parents might have if they’d just had a child, and saw social value in religion even though they doubted its metaphysical truth. I’ve known people who were in this exact position.
I was in Provo, Utah, a little while ago. It seemed like a movie scene depicting what America was like in the 1950s. Everyone was white. Everyone was clean cut, and friendly, and tastefully dressed. Everyone was polite, and nobody swore when talking. Brigham Young University, near where I was staying, has student policies against long hair and beards. I had both, but nobody I spoke to mentioned it, let alone displayed any hostility on that account.
Apparently everyone gets married quite young. I went skiing at a nearby mountain, and in the line on the chairlift, I stood behind two young men (for some reason, the term boys doesn’t seem appropriate) who couldn’t be more than 23 or so, perhaps younger. One was telling the other about the importance of making sure you got along well with the family of the girl you wanted to marry, given how much time you would be spending with them (although sometimes you love someone who doesn’t fall in that category). He offered the insight, which I thought quite perceptive, that mothers tended to like girlfriends who were somewhat like themselves, if for no other reason than that they feel they understand the girl better.
I cannot imagine such a conversation among 23 year old boys in most parts of this country. To most of them, the whole concept would be literally inconceivable. That I would not have wanted to get married by 23 does not detract at all from the fact that I think society is better off if more people married by 25 and had three or four kids, rather than getting married at 35 (if at all ) and having one or none.
But what I remember most vividly was when I was walking back from a restaurant in Provo. I walked past a young 20-something couple (probably married) who were about to walk into the restaurant. They were approached by a slightly older grizzled white guy with a long beard carrying a duffle bag. The beard guy asked the young man which way the bus station was. The young man told him it was a few blocks away, and gave him directions.
The older man thanked him, and started walking. He had gotten perhaps 10 metres when the young man came running up. ‘Look’, he said, ‘it’s a bit of a walk. Why don’t I just drive you there?’. ‘Are you sure?’ asked the old man. ‘Yeah, it’s no problem at all.’, the young man replied.
Reader, can you imagine this conversation playing out that way in the city or town where you live? In the context of Provo, the whole affair didn’t seem out of place at all.
What that young man believed about the afterlife troubles me not one jot. As Mr Jefferson put it, it does me no injury for my neighbor to say there are twenty gods or no God. It neither picks my pocket nor breaks my leg. But how that man acts to his fellow man is a subject that interests me considerably.
People like that young man are what’s great about America, actually. I would want them as my neighbors. All I know is that Mormonism seems to regularly produce people like that, and this is something that warms my heart. If a metaphysical belief in magic undergarments is the necessary price to pay to make this happen, I would pay it enthusiastically.
And the critiques are well-rehearsed.
Militant atheists like to mock Mormonism’s odd beliefs about the universe, amply documented (in otherwise quite fair and sympathetic portrayals) in Southpark and The Book of Mormon. The beliefs themselves, including disappearing golden tablets and the like, are not really much more absurd than many other religions. But they are claimed to have happened more recently, which seems to make an unusually large difference. Partly this makes certain events easier to disprove, but I don’t think that’s really it. I think actually most of the difference in perception is psychological. To the rationalist, it is no more plausible that Jesus turned water into wine two thousand years ago than that I turned water into wine yesterday. To the common person, however, the latter seems to require a larger suspension of disbelief – the rest of the scene is suddenly palpable and gets compared with what we know about the modern world. For some reason, with old religions, part of the brain thinks ‘well, who knows what things were like back then’.
Social Justice types tend to berate Mormons for their socially conservative views. They dislike abortion, they dislike gay marriage, they tend to hold to quite traditional views of gender roles. Add in desired talking points to taste on whatever side you like here and this writes itself. I do note, however, that the volume of the criticism they receive seems better explained by the fact that they’re a soft target in social terms and won’t fight back. After Proposition 8 passed in California, lefties angrily protested against the Mormons (who supported it on average), but not against Blacks and Hispanics who also supported it on average (the same is probably true of Muslims too). Interpret how you will.
Myself, I’ve always been far more struck by something much simpler. Nearly all the Mormons I’ve ever met have been really friendly, nice people. And that matters to me, a lot. We’re talking maybe n=20 or 30 by this point. How many groups of people, in any category, can you honestly say that about?
If I were to choose a religion based purely on the personal qualities and behavior of its average adherent, I’m pretty sure that I’d pick Mormonism.
This hypothetical is less absurd than it sounds. It actually corresponds fairly closely to the thought process that atheist parents might have if they’d just had a child, and saw social value in religion even though they doubted its metaphysical truth. I’ve known people who were in this exact position.
I was in Provo, Utah, a little while ago. It seemed like a movie scene depicting what America was like in the 1950s. Everyone was white. Everyone was clean cut, and friendly, and tastefully dressed. Everyone was polite, and nobody swore when talking. Brigham Young University, near where I was staying, has student policies against long hair and beards. I had both, but nobody I spoke to mentioned it, let alone displayed any hostility on that account.
Apparently everyone gets married quite young. I went skiing at a nearby mountain, and in the line on the chairlift, I stood behind two young men (for some reason, the term boys doesn’t seem appropriate) who couldn’t be more than 23 or so, perhaps younger. One was telling the other about the importance of making sure you got along well with the family of the girl you wanted to marry, given how much time you would be spending with them (although sometimes you love someone who doesn’t fall in that category). He offered the insight, which I thought quite perceptive, that mothers tended to like girlfriends who were somewhat like themselves, if for no other reason than that they feel they understand the girl better.
I cannot imagine such a conversation among 23 year old boys in most parts of this country. To most of them, the whole concept would be literally inconceivable. That I would not have wanted to get married by 23 does not detract at all from the fact that I think society is better off if more people married by 25 and had three or four kids, rather than getting married at 35 (if at all ) and having one or none.
But what I remember most vividly was when I was walking back from a restaurant in Provo. I walked past a young 20-something couple (probably married) who were about to walk into the restaurant. They were approached by a slightly older grizzled white guy with a long beard carrying a duffle bag. The beard guy asked the young man which way the bus station was. The young man told him it was a few blocks away, and gave him directions.
The older man thanked him, and started walking. He had gotten perhaps 10 metres when the young man came running up. ‘Look’, he said, ‘it’s a bit of a walk. Why don’t I just drive you there?’. ‘Are you sure?’ asked the old man. ‘Yeah, it’s no problem at all.’, the young man replied.
Reader, can you imagine this conversation playing out that way in the city or town where you live? In the context of Provo, the whole affair didn’t seem out of place at all.
What that young man believed about the afterlife troubles me not one jot. As Mr Jefferson put it, it does me no injury for my neighbor to say there are twenty gods or no God. It neither picks my pocket nor breaks my leg. But how that man acts to his fellow man is a subject that interests me considerably.
People like that young man are what’s great about America, actually. I would want them as my neighbors. All I know is that Mormonism seems to regularly produce people like that, and this is something that warms my heart. If a metaphysical belief in magic undergarments is the necessary price to pay to make this happen, I would pay it enthusiastically.
Sunday, February 21, 2016
Failure
There is an odd camaraderie among those who have failed.
I’ve been finding this out recently (which is the reason for
the paucity of recent posts).
I used to be fairly insouciant about the prospect of getting
fired. Then I got fired, and I suddenly had a lot more sympathy for people who
seemed to be quite upset for a period afterwards. Like so many misfortunes in
life, it’s easy to be glib about it until it happens to you. But when it does,
you remember it.
Life does indeed go on, and I’m in a good position
employment-wise. I initially decided that stoicism was the way forward, and asserted (part aspirationally) that everything was fine. ‘Whine less’ was already the motto of 2016, inspired by Epictetus's 'Discourses'. I
stand by that motto, incidentally. But after a few days of hassling around
emailing people and getting a good mix of polite but awkward refusals (along
with some interest), I finally was a bit down. Now I’m actually getting towards
the point I claimed to be at initially.
In the process of emailing work friends about the prospect
of getting a job, when I explained the circumstances of my departure I got a
surprising number of quite heartfelt responses. When I went through the list of
who wrote back like this, I realised that a lot of them had gone through the
same thing at one point. ‘I know how it feels’, one wrote. He wasn’t lying.
The last time I remember this happening was years ago when I
was about 20, and working at my Dad’s office. There was an early 30’s guy there
whom I got along with well, and looked up to in the way of young men
who engage on somewhat jovial mockery and discussion. On a Saturday afternoon,
when I was leaving the office, I told him that I was off to break up with my
girlfriend. I expected him to make a joke, or some sort of bonhomie about the
prospective fun of being single again. But his response was nothing of the
sort. ‘That sucks man, I’m really sorry’, was his reply. Having not had a
serious breakup before then, I found it a little unexpected, but didn’t think
too much of it. 3 hours of break-up conversation later, I understood the
kindness of his response a lot more.
The whole recent experience has made me want to be kinder to
the people around me.
I think that’s a good addition to the 2016 motto as well,
actually.
Sunday, January 24, 2016
Your Opinion Doesn't Matter
In the psychology of the west in the 21st century, two characteristics predominate.
First, this is the age of democracy.
Second, this is the age of narcissism.
And the coexistence of both does not seem to be a coincidence.
As far as I can tell, the actual value of holding regular elections is to flatter the conceit of the individual voters so that they feel important and don't revolt. Look at these powerful people, groveling to you, promising you things! They're in a VFW Hall somewhere in Ohio, eating terrible rubber chicken, nodding and pretending to care about your concerns. Some day they'll be president, but right now they're kissing your @$$. Admittedly, all the voting you did in the past somehow didn't manage to solve your problems, but surely this time will be different.
The slogan for all this nonsense is 'your opinion matters'. This comes in minor variants like 'your voice matters' or 'your vote matters', but the 'opinion' version is the favored generic variant. This is because 'opinion' requires the least possible effort on your part - you don't have to yell, like with a voice, or heaven forbid actually do something like waste an hour on some Tuesday in November. Your thoughts alone are so valuable that the powerful cannot wait to turn to you in order to hear them.
This is an obvious lie, easily identified as such.
The first clue is this exact phrase is frequently used by spam marketers trying to get you to click on online polls. It's almost like they've figured out that people are susceptible to empty flattery about the importance of their political opinions, and use this to infect their computers with malware. Hey, if they'll turn up when the government pulls this nonsense, why not us too? You can hardly blame them for thinking this, not least because they tend to be right.
But more importantly, the idea that your opinion matters violates the poker rule of relative naivete. The old advice in poker was that at every table, there is a mark - a rube or fool who doesn't know how to play the game, and that people will target to make money off. Play a few hands at a table. If after that time you haven't figured out who the mark is, the mark is you, and you should probably leave.
So in the game of politics, do you know who the mark is? Do you know who is being conned in the political process? Doubt not that professional politicians know who they think is being conned. The rich donors know who they think is being conned. The professional political advisers and lobbyists know who they think is being conned. Admittedly, they may not agree with respect to the position of each other - like in any poker game, overconfidence is rife, and most people think they're the best player at the table.
But they also all agree that one of the people clearly being conned is you, John Q. Citizen voter and taxpayer. And be honest - you don't have a clear idea of who is being conned, do you Citizen? Should this concern you? I feel it should.
I do like asking ardent demotists if their voice matters. They usually laugh, knowing the inherent ridiculousness of the question, but are reluctant to explicitly disclaim it.
Not only does your voice not matter individually, your voices barely even matter collectively. The permanent establishment of the civil service, courts, media and universities will continue on their merry way regardless. This is why you can elect Obama and find out, puzzlingly, that eight years later Guantanamo is still open and Americans are still dying in Iraq and Afghanistan. And this is in foreign policy, where the president apparently has the most freedom of action.
But in case the appeal to the importance of your ideas fails, there is a second plank of appeal to the importance of voting - that it is your civic duty. And people who may scorn the first appeal nonetheless seem susceptible to the second. To wit, voting shows how noble and civic-minded you are. Do you love your society? Then waste an hour of your life pressing a button for whichever of the two fools on stage you happen to detest less. Surely you are too responsible to not vote, citizen?
It's narcissism all the way down.
When I started reading more reactionary literature and being convinced by the arguments therein, it was oddly relieving to find out that my opinion does not matter. One no longer needs to feel personally involved or aggrieved by any of the nonsense of the political process. I feel no need to waste any more hours of this short and rapidly passing life worrying about exactly what Donald Trump did or didn't say in the most recent news cycle.
That's for the marks who feel that their vote matters.
This may sound like a call to passivism, that nothing at all matters, but it is not.
Your actions may very well matter. This is particularly true if enough of you act together.
But pressing the button for Kang or Kodos every four years seems unlikely to be one such action.
First, this is the age of democracy.
Second, this is the age of narcissism.
And the coexistence of both does not seem to be a coincidence.
As far as I can tell, the actual value of holding regular elections is to flatter the conceit of the individual voters so that they feel important and don't revolt. Look at these powerful people, groveling to you, promising you things! They're in a VFW Hall somewhere in Ohio, eating terrible rubber chicken, nodding and pretending to care about your concerns. Some day they'll be president, but right now they're kissing your @$$. Admittedly, all the voting you did in the past somehow didn't manage to solve your problems, but surely this time will be different.
The slogan for all this nonsense is 'your opinion matters'. This comes in minor variants like 'your voice matters' or 'your vote matters', but the 'opinion' version is the favored generic variant. This is because 'opinion' requires the least possible effort on your part - you don't have to yell, like with a voice, or heaven forbid actually do something like waste an hour on some Tuesday in November. Your thoughts alone are so valuable that the powerful cannot wait to turn to you in order to hear them.
This is an obvious lie, easily identified as such.
The first clue is this exact phrase is frequently used by spam marketers trying to get you to click on online polls. It's almost like they've figured out that people are susceptible to empty flattery about the importance of their political opinions, and use this to infect their computers with malware. Hey, if they'll turn up when the government pulls this nonsense, why not us too? You can hardly blame them for thinking this, not least because they tend to be right.
But more importantly, the idea that your opinion matters violates the poker rule of relative naivete. The old advice in poker was that at every table, there is a mark - a rube or fool who doesn't know how to play the game, and that people will target to make money off. Play a few hands at a table. If after that time you haven't figured out who the mark is, the mark is you, and you should probably leave.
So in the game of politics, do you know who the mark is? Do you know who is being conned in the political process? Doubt not that professional politicians know who they think is being conned. The rich donors know who they think is being conned. The professional political advisers and lobbyists know who they think is being conned. Admittedly, they may not agree with respect to the position of each other - like in any poker game, overconfidence is rife, and most people think they're the best player at the table.
But they also all agree that one of the people clearly being conned is you, John Q. Citizen voter and taxpayer. And be honest - you don't have a clear idea of who is being conned, do you Citizen? Should this concern you? I feel it should.
I do like asking ardent demotists if their voice matters. They usually laugh, knowing the inherent ridiculousness of the question, but are reluctant to explicitly disclaim it.
Not only does your voice not matter individually, your voices barely even matter collectively. The permanent establishment of the civil service, courts, media and universities will continue on their merry way regardless. This is why you can elect Obama and find out, puzzlingly, that eight years later Guantanamo is still open and Americans are still dying in Iraq and Afghanistan. And this is in foreign policy, where the president apparently has the most freedom of action.
But in case the appeal to the importance of your ideas fails, there is a second plank of appeal to the importance of voting - that it is your civic duty. And people who may scorn the first appeal nonetheless seem susceptible to the second. To wit, voting shows how noble and civic-minded you are. Do you love your society? Then waste an hour of your life pressing a button for whichever of the two fools on stage you happen to detest less. Surely you are too responsible to not vote, citizen?
It's narcissism all the way down.
When I started reading more reactionary literature and being convinced by the arguments therein, it was oddly relieving to find out that my opinion does not matter. One no longer needs to feel personally involved or aggrieved by any of the nonsense of the political process. I feel no need to waste any more hours of this short and rapidly passing life worrying about exactly what Donald Trump did or didn't say in the most recent news cycle.
That's for the marks who feel that their vote matters.
This may sound like a call to passivism, that nothing at all matters, but it is not.
Your actions may very well matter. This is particularly true if enough of you act together.
But pressing the button for Kang or Kodos every four years seems unlikely to be one such action.
Friday, January 15, 2016
On the lessons of fall of Rome
To anyone of a vaguely reactionary persuasion, the fall of Rome is a melancholy and tantalising story. The inescapable conclusion, no matter how exactly you explain the fall, is that progress is neither inevitable nor irreversible. Civilisation is fragile, and can be destroyed by a sequence of wrong decisions.
This fact used to be widely appreciated - empires and civilisations were considered to be subject to cycles of rise, power, decay and fall. You can see this, for instance, in Thomas Cole's series of paintings, "The Course of Empire", painted between 1833-1836.
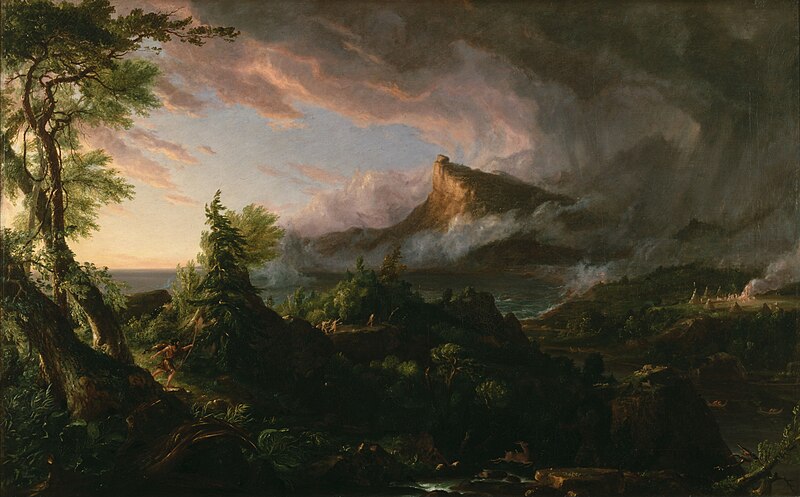

The Savage State
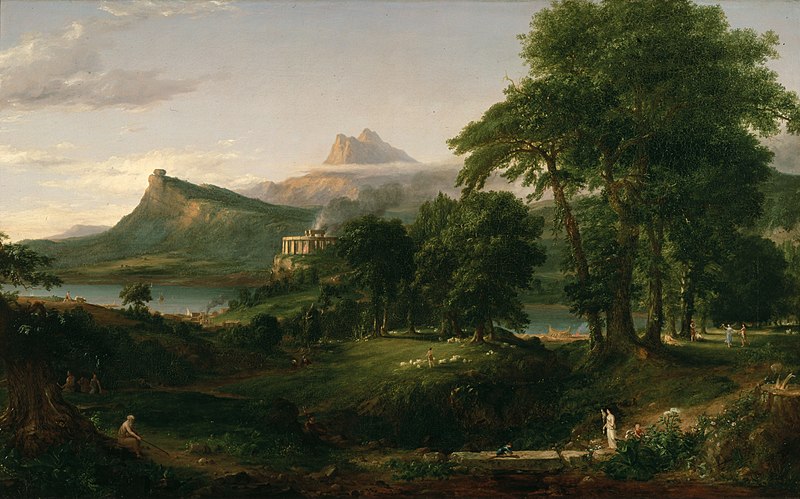

The Arcadian or Pastoral State

The Consummation of Empire

Destruction

Desolation
Of course, we live in an age where Whig history is the only history there is. Americans seem to contemplate the possible end of the glorious American experiment the way most people contemplate death. That is to say, not very often. And when they do, usually only when pressed on the issue, they'll acknowledge that it probably will happen eventually, but then they act as if it is only likely to occur in a very long time.
Then again, that's what the Romans thought too.
Which, to the conservative, makes the matter more alarming. Thinking you're not about to collapse and be overrun is a relatively weak indicator that you aren't, in fact, about to collapse and be overrun.
And in some sense, the modern American position is less forgivable than the Roman one. Today, we have the Romans as an example to consider. When Rome fell, there had not been any comparably long-lived Empire that had ever gotten that far, let alone one that had and had subsequently collapsed.
And while the inevitability of decay is true, the timeline iteslf is not. The other view is the less fatalistic one - try to figure out what exactly Rome did wrong, and try to make sure the same mistake isn't made again, to at least cheat the reaper a little longer. Such as not letting in barbarian hordes in numbers so large that they can sack your capital.
This is true, and a very useful exercise. But it's necessarily quite speculative. Why, exactly, did Rome let in the Goths, and could that have been changed? Harder to say. Would it have fallen anyway at some subsequent point not too long after? Even harder to say.
But there is one lesson that does seem useful, if understudied.
As I've written about before, the major blind spot of many Europeans (pace the Greeks) is that they equate the end of Rome with the end of the Roman Empire. But this was only the end of the Western Roman Empire. The Eastern Roman Empire, in Byzantium, continued on for roughly another thousand years. It may not have advanced to the same heights as the former, but you'd much rather be living there in 483AD than in Rome.
Which seems to suggest that if the collapse is coming, partition and separation may offer a better chance for partial survival.
The attitude of the West on these matters begins to resemble the process that Paul Fussell described pithily, if depressingly, about World War I:
This "slowly dawning and dreadful realisation" usually occurs as a result of two stages of rationalization and one of accurate perception:
1. It can't happen to me. I am too clever / agile / well-trained / good-looking / beloved / tightly laced / etc.
This persuasion gradually erodes into:
2. It can happen to me, and I'd better be more careful. I can avoid the danger by keeping extra alert at all times / watching more prudently the way I take cover or dig in or expose my position by firing my weapon / etc.
This conviction attenuates in turn to the perception that death and injury are matters more of bad luck than lack of skill, making inevitable the third stage of awareness:
3. It is going to happen to me, and only my not being there is going to prevent it.An individual may pack up and move, of course, but a country cannot.
A region can, however, choose to not be part of the same dysfunctional polity that is about to collapse.
Easier said than done, unfortunately. Rome had the virtue of having a Diocletian. America, however, does not.
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)
